As the initial military equipment, radar has now spread to the commercial market and is widely used in various fields such as industry, communications, and consumption. So, what exactly is radar?
In short, Radar (Radio DetecTIon and Ranging) is a radio device that discovers targets and measures their spatial position. It is an electronic device that uses electromagnetic waves to detect targets. The Doppler shift formula is used to estimate the velocity of the object, the target distance or range is calculated by the electromagnetic wave measured value, the target direction and angle are calculated by the antenna phase difference, and the target position is calculated by FMCW (Frequency Modulated ConTInuous Wave). It has many different application directions, including the development of hot drones, unmanned aircraft, and even gesture recognition on smartphones and wearable devices.
In addition, the radar can calculate the information of many physical quantities. As far as the design is concerned, in addition to the complete hardware composition, the algorithm and algorithm are also important.
As a radar application with more than 10 years experience, Infineon, which is known for its 24 GHz and 77 GHz in automotive radar, Mr. Mai Zhengqi, Director of RF and Sensors Division, Greater China, Power Management and Diversified Markets Division, in the 7th EEVIA Year The China ICT Media Forum and 2018 Industry and Technology Outlook Seminar gave a detailed introduction to the technology, development and application of radar.

Hardware composition
Figure 1 shows the basic hardware components of a radar system, including transmitters, receivers, signal processors, and antennas. When the radar is working, the transmitter generates a radio frequency electrical signal, and the electrical signal (electric energy) is converted into an electromagnetic wave through the antenna, and the receiver of the other radar receives the radio frequency signal, converts the radio frequency electrical signal into a low frequency signal, and then is processed by the signal. The device extracts the distance, velocity and angle from the signal to complete the working circuit. Of course, to actually operate the radar, you also need internal algorithms and GUI interfaces.
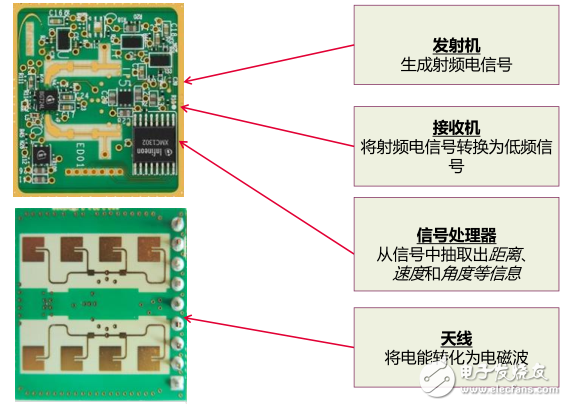
Figure 1 Basic hardware components of the radar system
Operating modeDepending on the function, the radar can be divided into several working modes. Among them, Table 1 shows the working modes of the main applications of the three industrial radars.
Table 1 Working modes of the main applications of three industrial radars
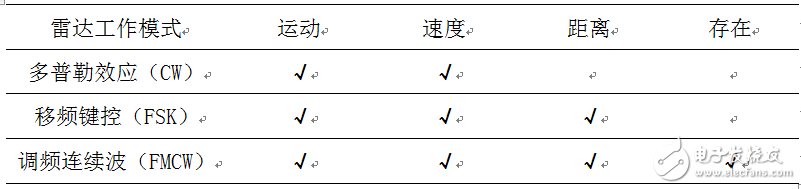
For different functions and applications, when your design only needs to detect object speed or motion, you can use the simple Doppler effect in the algorithm part, which is relatively easy to implement; when your design needs to detect objects When you need to use distance, you must use FSK. When your design needs to detect the presence of static objects, you must use FMCW. The corresponding algorithm complexity is: CW-FSK-FMCW. As the complexity of the algorithm deepens, the cost of the solution and its computational power consumption increase accordingly. Therefore, the application of complex algorithms has always been a large application of radar. The challenge.
Millimeter wave radarThe millimeter wave refers to an electromagnetic wave having a wavelength of 1 to 10 mm, which is located in a wavelength range in which the microwave and the far infrared wave overlap, and thus has the characteristics of both kinds of spectra. At present, millimeter waves mainly have two applications of data transmission and radar detection. Among them, in radar, blind spot detection (BSD) is an application of its rapid growth, and its main application in the automotive industry, as shown in Figure 2 is the global 24GHz BSD demand trend.
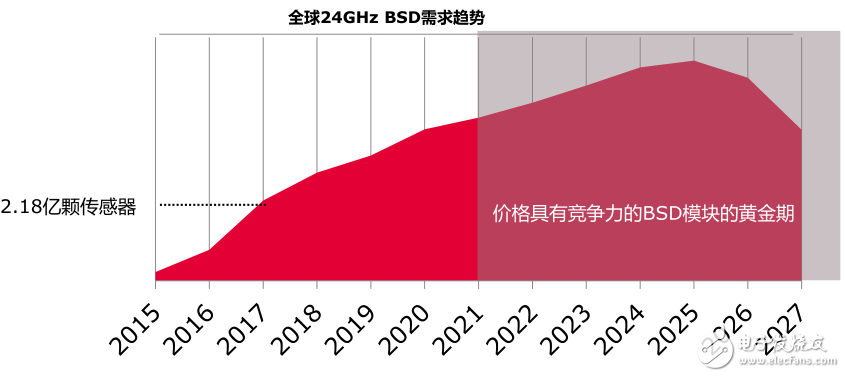
Figure 2 Global 24GHz BSD Demand Trend Chart
As can be seen from Figure 2, there are 218 million sensors applied to this BSD in 2017, so the market demand for millimeter wave radar has increased significantly. As far as BSD is concerned, as the product matures and its competitiveness increases, the millimeter wave radar will enter a period of rapid development after 2020.
Three major challenges facing millimeter wave radarThe application of millimeter wave radar now also has three major challenges.
Some applications in the industry have been replaced by some infrared, laser radar, and independent solutions. Although the market for millimeter wave radar is still growing in terms of market, some applications cannot be ignored by other solutions.
The need for custom algorithms. This is also the main challenge of millimeter wave radar applications. Different applications require different algorithms, and different algorithms require different experts to do research and development, which brings great troubles for the development of specific applications of millimeter wave radar.
The millimeter wave band regulations are not yet clear. Because the millimeter wave is a relatively high frequency band, in terms of radio specifications, the regulations and policies formulated by various countries and regions have not been completely defined, especially when these millimeter waves have not been fully used. Band. 5G may also use millimeter waves, which may use different frequency bands such as 28GHz, 29GHz, 39GHz, etc. How to make different definitions and specifications between frequency bands and frequency bands, which are clearly defined by the relevant regulations.
Frequency band selectionAll radars operate in specific frequency bands ranging from 300MHz to 300GHz. The daily applications mainly use the 2.4GHz~200GHz frequency band (Figure 3), and each frequency band is such as antenna size, application range, wavelength, Penetration affects radar, and each country has a different definition of these bands. For example, microwave ovens are used at 2.4 GHz, mobile applications are in the range of 2 GHz to 3 GHz, industrial applications are mainly at 24 GHz and 60 GHz, and automobiles are mainly used at 77 GHz.
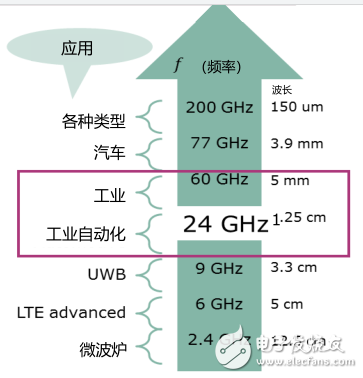
Figure 3 Working frequency band for each application
Among them, the higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength, and the shorter the wavelength, the higher the resolution and accuracy. The common 24GHz wavelength is 31.25px, the 60GHz is 5mm, and the 2.4G wavelength is 312.5px. Radar is applied to different scenes using short-wave characteristics.
24GHz and 60GHz radars are used in the field of intelligenceMore discussion now is on the application of 24GHz and 60GHz radars in many intelligent emerging applications.
Among them, 24GHz mainly implements space and motion sensing, including application to smart homes, smart buildings, smart home appliances, intelligent monitoring, etc., applied to personnel/object presence, counting, position, speed, and anti-collision and vital sign sensing, such as some People also use 24 GHz radar in the medical field to detect physical signs such as heartbeat and breathing. Among them, the radar antenna design is more flexible, engineers can make different antenna designs according to different scenarios.
The 60 GHz radar has higher frequency and shorter wavelength, so it can be applied not only to the applicable scene of 24 GHz, but also because the antenna can be designed to be smaller, and the external environment is less disturbed, which has advantages in human-computer interaction and gesture recognition. .
Among them, in gesture recognition, Infineon and Google Advanced Technology and Projects (ATAP) team jointly developed a radar-based sensing solution IC in the ProjectSoli cooperation project, which mainly uses small sensors designed by Infineon's 60GHz radar. Can be used in mobile phones or wearable devices for gesture recognition.

Figure 4 Small sensor application for Infineon's 60 GHz radar design
The development trend of vehicle radarVehicle radar has been used again with the development of autonomous driving. As far as the world's mainstream automobile industry is concerned, the front part must use 77GHz radar, while the side and reverse landscape detection mostly use 24GHz. Radar, which is currently the mainstream of the automotive industry worldwide. In China, the front-loading is still the mainstream of 77GHz, and the after-loading market is now using 24GHz, but in the pre-installation market, the joint development of 77GHz and 24GHz radar may be considered. When talking about whether to use 77GHz as a complete solution in the future, Mai Zhengqi said that we have also done a lot of discussions with the automotive industry group. From a technical point of view, it is difficult to complete in the short term. We believe that in the next 7 years. The side collision of the car is still dominated by the 24 GHz radar, because it has the advantage of above price or mature technology. It may extend to the side of the 77 GHz or the lateral collision avoidance of the back, but it is still subject to the following regulations. Look.
Infineon strengthens cooperation with domestic manufacturers
Mr. Mai Zhengqi said that Infineon provides a complete radar solution, so we must develop with some partners, especially in the software and applications. In the application of 24GHz radar, there are some successful cases in security applications, blind spot detection and smart home. The whole scheme and product design have been completed, and it is also marketed. In the future, we will continue to extend the application of millimeter wave radar to industrial 4.0, intelligent manufacturing, human-computer interaction, medical and other fields with more advanced Chinese manufacturers and more advanced ideas. This is also our two years. Ponder over a focus in the Chinese market.
ZGAR Vape Device 5.0
ZGAR electronic cigarette uses high-tech R&D, food grade disposable pod device and high-quality raw material. All package designs are Original IP. Our designer team is from Hong Kong. We have very high requirements for product quality, flavors taste and packaging design. The E-liquid is imported, materials are food grade, and assembly plant is medical-grade dust-free workshops.
From production to packaging, the whole system of tracking, efficient and orderly process, achieving daily efficient output. We pay attention to the details of each process control. The first class dust-free production workshop has passed the GMP food and drug production standard certification, ensuring quality and safety. We choose the products with a traceability system, which can not only effectively track and trace all kinds of data, but also ensure good product quality.
We offer best price, high quality Vape Device, E-Cigarette Vape Pen, Disposable Device Vape,Vape Pen Atomizer, Electronic cigarette to all over the world.
Much Better Vaping Experience!

ZGAR 5.0 E-Cigarette Vape Pen,ZGAR 5.0 Device Vape,ZGAR Vape Device 5.0 Vape Pen Atomizer,ZGAR Vape Device 5.0 Disposable E-Cigarette OEM vape pen,ZGAR Device 5.0 electronic cigarette
ZGAR INTERNATIONAL(HK)CO., LIMITED , https://www.szvape-pods.com